Introduction to varicose veins
Welcome to the ultimate guide on varicose veins! Have you ever noticed those twisted, bulging veins on your legs that seem to have a life of their own? Well, you’re not alone. Varicose veins affect millions of people worldwide and can be more than just a cosmetic concern. Let’s dive deep into what causes these pesky veins and how you can prevent and treat them effectively. So, sit back, relax, and let’s explore the world of varicose veins together!
Understanding the anatomy of the veins
Veins play a crucial role in our circulatory system, carrying blood back to the heart. Unlike arteries that have thick walls and carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart, veins have thinner walls and transport oxygen-depleted blood back to be re-oxygenated. Within our veins are tiny valves that help prevent the backward flow of blood. When these valves weaken or become damaged, it can lead to a condition known as venous insufficiency, causing blood to pool in the veins. This pooling of blood can increase pressure within the veins, leading to their enlargement and eventual bulging appearance – otherwise known as varicose veins. Varicose veins often occur in the legs where gravity makes it harder for blood to return to the heart efficiently. Understanding how these delicate valves function is key in grasping why varicose veins develop and how they can impact overall circulatory health.
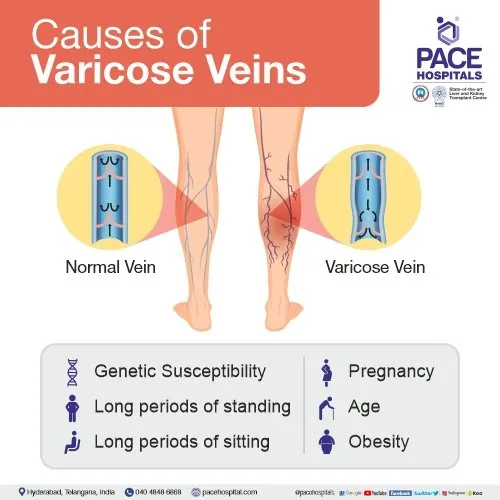
Genetics and family history as a cause of varicose veins
Varicose veins can sometimes feel like an inevitable part of our genetic makeup, passed down through family lines like hair color or height. The truth is that genetics and family history play a significant role in the development of varicose veins. If your parents or grandparents had them, you may be more predisposed to developing them yourself. Certain genetic factors can affect the strength and elasticity of your vein walls, making it easier for them to stretch and become varicose over time. While you can’t change your genes, being aware of your family history can help you take proactive steps to prevent or manage varicose veins. If varicose veins run in your family, it’s essential to stay vigilant about maintaining good circulation and keeping a healthy lifestyle. Regular exercise, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, and wearing compression stockings can all help reduce the risk of developing varicose veins – even if they seem written into your DNA.
Lifestyle factors that contribute to varicose veins
Our daily habits and lifestyle choices can play a significant role in the development of varicose veins. Leading a sedentary lifestyle, where we sit or stand for long periods without movement, can put extra pressure on our veins, leading to poor circulation and the potential development of varicose veins. Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial in preventing varicose veins as excess weight puts added strain on our circulatory system. Regular exercise can help improve blood flow and strengthen vein walls, reducing the risk of developing these unsightly bulging veins. Smoking has been linked to decreased blood flow and weakened vein health, making smokers more susceptible to varicose veins. Additionally, wearing tight clothing that restricts blood flow can exacerbate existing vein issues or contribute to their formation over time. Incorporating leg exercises into your routine, elevating your legs when resting, and avoiding crossing your legs for prolonged periods can all help reduce the likelihood of developing varicose veins due to poor circulation. Making small changes in our daily habits can go a long way in promoting healthier veins and overall well-being.
Pregnancy and hormonal changes as a risk factor
Pregnancy brings about a multitude of changes in a woman’s body, including an increased risk of developing varicose veins. The hormonal shifts during pregnancy can weaken the walls of the veins, causing them to dilate and become more visible beneath the skin. As the uterus grows, it puts pressure on the large vein on the right side of the body (the inferior vena cava), leading to poor circulation and potentially contributing to varicose veins. Furthermore, higher levels of progesterone relax the blood vessels, making it easier for them to swell and become varicose. The added weight gain during pregnancy also adds strain on the legs’ veins, exacerbating any existing venous issues or predispositions. While not all women will develop varicose vein during pregnancy, those with a family history are at an increased risk due to genetic predispositions compounded by hormonal changes. It’s essential for pregnant women experiencing discomfort from varicose veins to consult with their healthcare provider for guidance on managing symptoms and minimizing risks associated with this common yet bothersome condition.
Age and its impact on developing varicose veins
As we age, our veins may start to show signs of wear and tear. Varicose veins are not uncommon among the aging population. Over time, the valves in our veins that help blood flow back to the heart can weaken, leading to pooling of blood and visible varicose veins. The natural aging process can also cause a decrease in skin elasticity, making it harder for veins to return blood efficiently. This increased pressure can result in bulging varicose veins that are often more pronounced in older individuals. A sedentary lifestyle or prolonged periods of standing throughout one’s lifetime can exacerbate the effects of aging on vein health. As we grow older, these factors combined with genetic predispositions can increase the likelihood of developing varicose veins. It’s essential to be mindful of how age impacts our vascular health and take proactive measures such as regular exercise and proper leg elevation to support healthy circulation throughout life.
Other medical conditions that can lead to varicose veins
Varicose veins can also be linked to various medical conditions beyond genetics and lifestyle factors. Conditions like obesity, which increase pressure on the veins, can contribute to their development. Additionally, blood clots or deep vein thrombosis can obstruct proper blood flow and lead to varicose veins forming as a result. Certain inflammatory conditions such as vasculitis, which cause inflammation in the blood vessels, may also play a role in the onset of varicose veins. Hormonal imbalances related to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders could impact vein health and contribute to varicose vein formation. Moreover, individuals with a history of chronic venous insufficiency or vascular malformations are more prone to developing varicose veins due to compromised vein function. It’s essential for those with these medical conditions to be aware of the potential risk factors associated with varicose veins and seek appropriate treatment options when necessary.
Prevention and treatment options for varicose veins
When it comes to preventing varicose veins, there are several lifestyle changes you can make. Regular exercise like walking or swimming can help improve circulation and strengthen your leg muscles. Avoid sitting or standing for long periods without moving, as this can put extra pressure on your veins. Maintaining a healthy weight is also important in preventing varicose veins. Excess weight puts added strain on your circulatory system, making it harder for blood to flow efficiently through your veins. Eating a balanced diet rich in fiber and low in salt can also help support overall vein health. Compression stockings are often recommended for individuals with varicose veins as they apply gentle pressure to the legs, helping to improve circulation. Elevating your legs above heart level when resting can also aid in reducing swelling and discomfort associated with varicose veins. In terms of treatment options, minimally invasive procedures like sclerotherapy or endovenous laser treatment (EVLT) are commonly used to treat varicose veins. These procedures aim to close off the affected vein, redirecting blood flow to healthier ones. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the damaged vein altogether.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes of varicose veins is crucial in both prevention and treatment. Factors like genetics, lifestyle choices, pregnancy, age, and other medical conditions can all play a role in the development of varicose veins. By being aware of these potential triggers, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize their risk or seek appropriate medical intervention when needed. Remember that maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing positions, wearing compression stockings if necessary, and seeking professional advice when symptoms arise are key strategies for managing varicose veins. If you suspect you may be prone to developing varicose veins or if you already have them but are experiencing discomfort or complications, don’t hesitate to consult with a healthcare provider specializing in vein health. By staying informed about the causes and risk factors associated with varicose veins and taking preventive measures early on, you can better protect your vascular health and enjoy improved quality of life without the burden of this common condition.