Soil Mites are ubiquitous arthropods that occur in nearly all terrestrial habitats. They include a wide range of shapes, sizes, and colors, and can be found in nearly every type of soil. Soil mites play an important role in the decomposition of organic matter and the cycling of nutrients in terrestrial ecosystems. They are also important prey items for many predators, including spiders, birds, and small mammals. In this blog post, we will explore the different types of soil mites, their ecology, and their importance in the environment.
Soil Mites are small arthropods that live in the soil. They are related to spiders, ticks, and other mites. There are over 10,000 different species of soil mites, and they can be found on every continent except Antarctica. Soil mites play an important role in the environment by breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients. They also provide food for other animals, such as birds and rodents. In some cases, soil mites can become pests themselves, infesting homes and gardens. In this article, we will provide an overview of soil mites, their biology, and their importance in the environment.
What are Soil Mites?
Soil mites are small, soil-dwelling arthropods that feed on organic matter. They are an important part of the soil food web and play a role in decomposition and nutrient cycling. Soil mites are also valuable indicators of soil health.
There are two main groups of soil mites: oribatid mites and mesostigmatid mites. Oribatid mites are larger and more abundant in soils than mesostigmatid mites. Both groups of mites can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and agricultural fields.
Soil mites play an important role in decomposition by breaking down organic matter into smaller pieces that can be easily absorbed by plants. In addition, soil mites help to cycle nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus through the ecosystem. Soil mites also provide food for other animals, such as insects, spiders, and rodents.
Soil mites are sensitive to changes in their environment and can be used to monitor soil health. For example, increases in the number of soil mites may indicate that the soil is becoming drier or more compact. Decreases in the number of soil mites may indicate that the soil is becoming wetter or more nutrient-rich.
The Different Types of Soil Mites
There are two main types of soil mites: the Acari and the Oribatida. The Acari are the most common type of soil mite and can be found in nearly all types of habitats. They are small, typically less than 1 mm in length, and have a wide variety of shapes and colors. The Oribatida are a much smaller group of soil mites, with most species less than 0.5 mm in length. They are often dark-colored and have a more cylindrical shape than the Acari.
Soil mites play an important role in the decomposition of organic matter and the recycling of nutrients in ecosystems. They are also a key food source for many other animals, including insects, spiders, reptiles, and small mammals.
The Life Cycle of a Soil Mite
Soil mites are small arthropods that live in the upper layers of soil. They are important members of the soil food web and play a role in decomposition and nutrient cycling. Soil mites are very diverse, with over 10,000 species described worldwide.
The life cycle of a soil mite begins with an egg. The egg hatches into a larva, which goes through several stages of growth before becoming an adult. The adults reproduce and lay eggs, starting the cycle anew.
Soil mites generally have a short lifespan, ranging from a few weeks to a few months. However, some species can live for up to two years. Soil mites are an important part of the ecosystem and perform many vital functions.
What do Soil Mites Eat?
Soil mites are small arthropods that live in the soil. They are a type of predator that feeds on other small animals, such as insects, nematodes, and other arthropods. Soil mites are important members of the soil community, as they help to control populations of pest species.
How do Soil Mites Reproduce?
Soil mites are small arthropods that can be found in many different types of habitats. They are often found in soil, but can also live in other places such as leaf litter and decaying wood. Soil mites are important for the recycling of organic matter and the aeration of the soil.
Most soil mites reproduce sexually, with both males and females present in populations. Mating usually occurs in the spring or summer months. After mating, females lay eggs in the soil or other substrate. The eggs hatch into larvae, which go through several molts before reaching adulthood. Depending on the species, adults may live for several months to a year.
What are the Predators of Soil Mites?
There are many predators of soil mites, including other mites, centipedes, millipedes, springtails, ants, spiders, and beetles. These predators help to keep the soil mite population in balance and help to control any outbreaks of soil mites.
What are the Pests of Soil Mites?
There are many different types of soil mites, and each has its own specific set of pests. The most common soil mite pests include:
• Acari: These tiny mites are the most common type of soil mite pest. They feed on organic matter in the soil, and can quickly reproduce in large numbers. Acari can be controlled with regular applications of insecticide.
• Fungi: Soil mites are often hosted to various types of fungi, which can cause disease in plants. Fungal diseases of soil mites include root rot and mildew. Fungi can be controlled with fungicides.
• Bacteria: Soil mites can also carry bacteria, which can be harmful to plants. Bacterial diseases of soil mites include crown rot and blight. Bacteria can be controlled with antibiotics.
How Do You Control Soil Mites?
One of the most effective ways to control soil mites is to reduce the amount of organic matter in the soil. This can be done by tilling the soil and/or using chemicals such as fumigants. Other methods of control include flooding, solarization, and using beneficial nematodes.
Conclusion
Soil mites are tiny creatures that play an important role in the decomposition of organic matter and the recycling of nutrients in the soil. They are also a valuable food source for many animals, including birds, reptiles, and amphibians. Although they are small, soil mites can have a big impact on the health of your garden or lawn. If you think you have a problem with soil mites, there are several things you can do to get rid of them.
 Unlock Your Path to Beauty, Wellness & Success
Unlock Your Path to Beauty, Wellness & Success 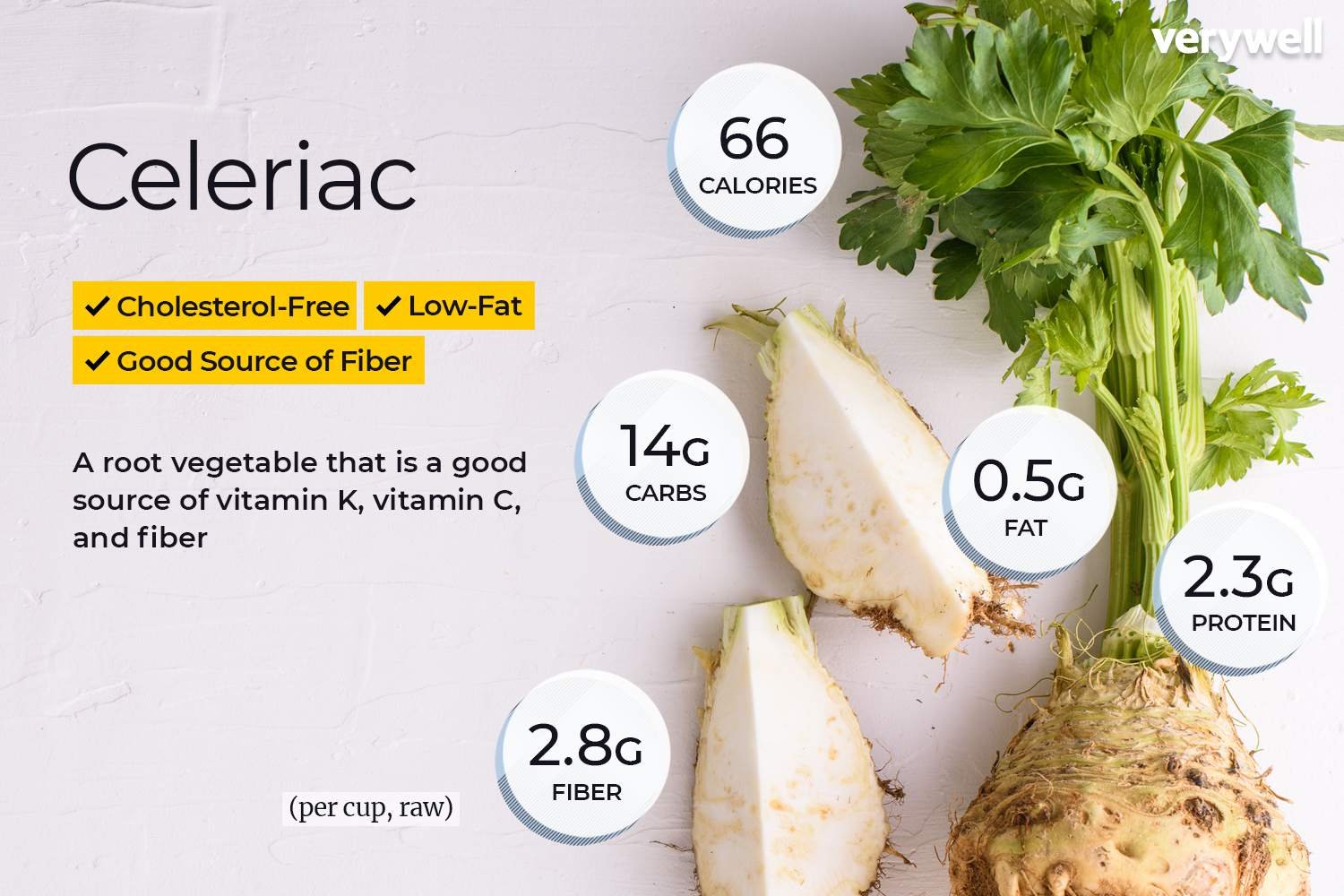 Pravi Celer: The Real Celery Explained with Benefits, Uses, and Nutrition Facts
Pravi Celer: The Real Celery Explained with Benefits, Uses, and Nutrition Facts  Pragmatic Juara100.org Medal: Everything You Need to Know
Pragmatic Juara100.org Medal: Everything You Need to Know  Understanding repmold: The Future of Sustainable Manufacturing
Understanding repmold: The Future of Sustainable Manufacturing  Rowdy Oxford Integris: Pioneering a New Era in Education and Innovation in 2025
Rowdy Oxford Integris: Pioneering a New Era in Education and Innovation in 2025  EO Pis: The Modern Framework for Executive Performance Insights
EO Pis: The Modern Framework for Executive Performance Insights